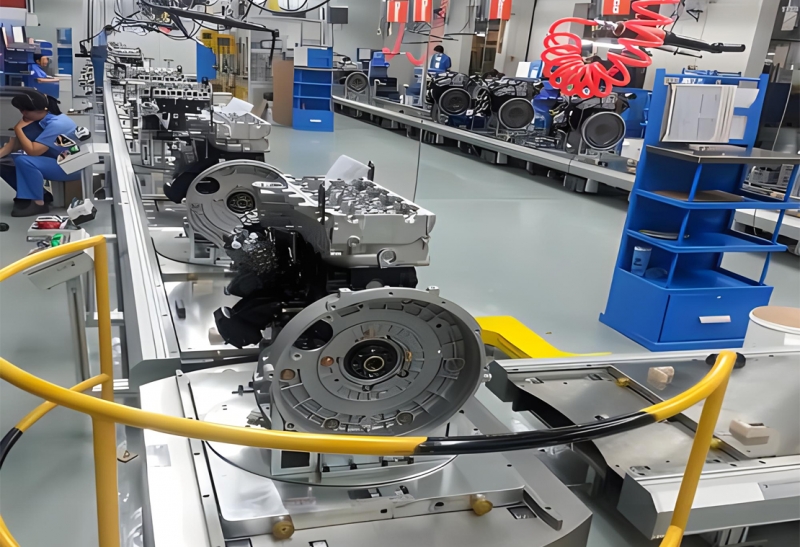
Engine Generation Assembly Line
| Name: | Engine Generation Assembly Line |
| Application: | Produce engines for various applications |
| Model: | HZ-AS0112 |
| Customization: | Available |
| Inquiry |
Product Description
An Engine Generation Assembly Line refers to a manufacturing system designed to produce engines for various applications such as automotive vehicles,
industrial machinery, generators, and more. Here's a breakdown of the process typically involved in an engine generation assembly line:
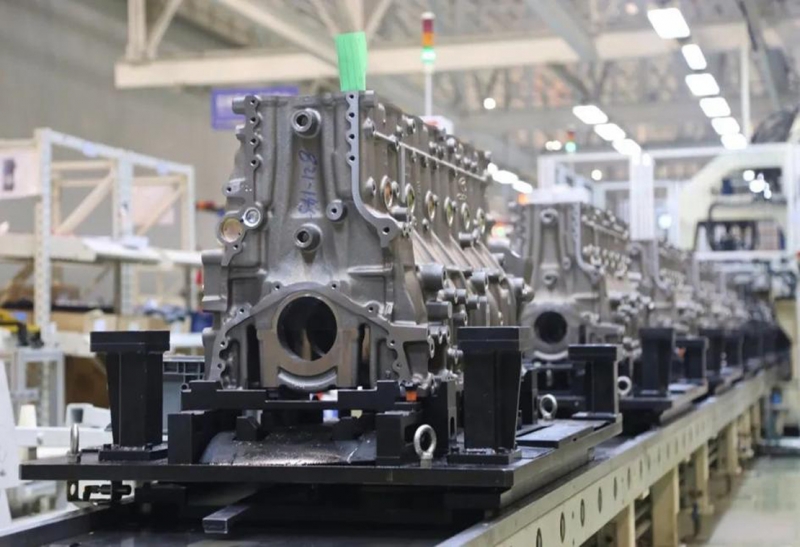
1. Component Procurement: The production process begins with the procurement of raw materials and components required for building the engine. This includes engine blocks, cylinder heads,
pistons, crankshafts, camshafts, valves, bearings, gaskets, seals, and other essential parts.
2. Sub-Assembly: Different components of the engine are assembled into sub-assemblies. For example, the cylinder head assembly, piston assembly, crankshaft assembly,
and timing system assembly are prepared separately before being integrated into the final engine assembly.
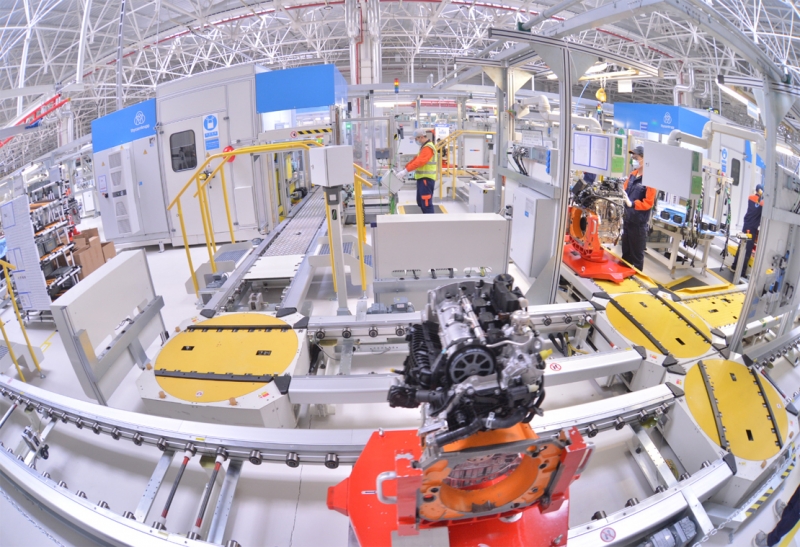
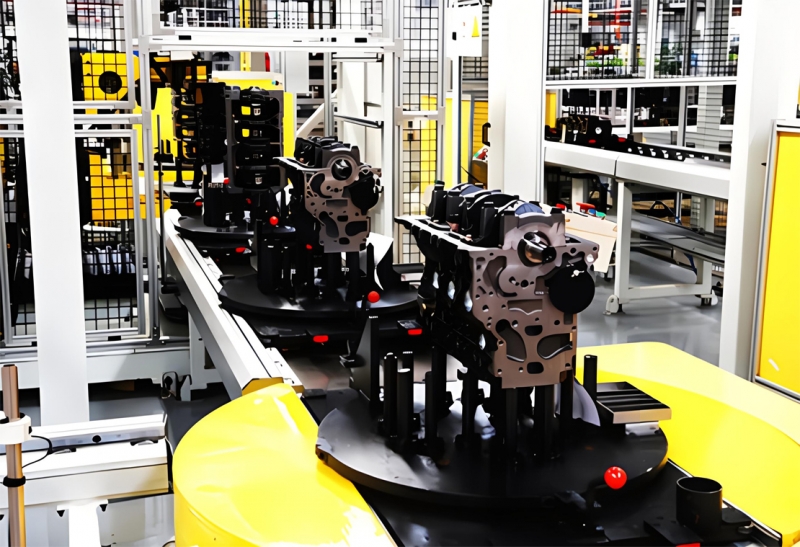
3. Main Assembly: The main assembly line is where the sub-assemblies are brought together to form the complete engine. This involves precise fitting and alignment of components according
to the engine's specifications and design requirements.
4. Precision Machining: Specialized machinery is often used for precision machining operations such as boring, honing, milling, and grinding to ensure the accuracy and smooth operation of critical
engine components.
5. Testing and Quality Control: Throughout the assembly process, engines undergo rigorous testing and quality control checks to ensure they meet the required performance, reliability, and safety standards.
This includes tests for compression, leakage, torque, vibration, temperature, and emissions.
6. Final Inspection and Packaging: Once assembled and tested, engines undergo final inspection to verify that they meet all quality standards. They are then securely packaged and prepared for distribution to
customers or installation in vehicles, machinery, or other equipment.
7. Automation and Robotics: Many modern engine generation assembly lines incorporate automation and robotics to streamline production, increase efficiency, and improve consistency in assembly processes.
Robots may be used for tasks such as component handling, welding, fastening, and inspection.
Overall, an engine generation assembly line requires meticulous planning, skilled labor, advanced machinery, and stringent quality control measures to ensure the production of
high-quality engines that meet performance requirements and customer expectations.







 Send Email
Send Email smartproductionlines
smartproductionlines